While solar eclipses have existed ever since the moon was formed — which scientists say happened several billion years ago — humans’ understanding of the eclipse is more recent. Below are answers to some common questions about eclipses.
WHAT CAUSES AN ECLIPSE?
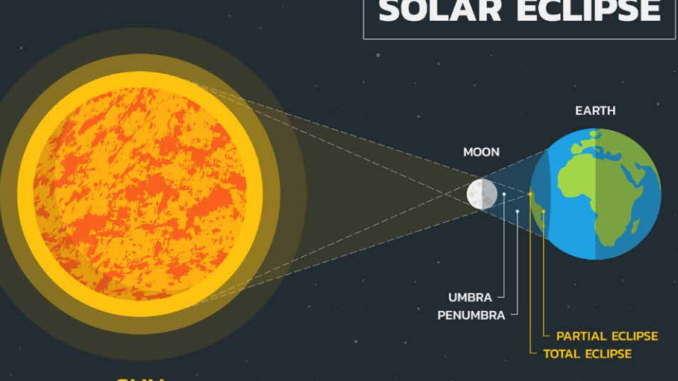
Eclipses are caused by the alignment of the sun, Earth and moon. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s path falls between Earth and the sun, blocking out sunlight for a period of time.
CAN I WATCH IT ONLINE?
Yes. If the skies are cloudy or your job keeps you working at a desk, many science-themed websites are planning to livestream the eclipse via video as it happens.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE IN A PARTIAL AND TOTAL ECLIPSE?
A total eclipse occurs when the sun is completely blocked by the moon’s path, revealing the corona that normally cannot be seen with the naked eye. In a partial eclipse, the moon passes the sun off center so that a portion of the sun’s disk is still visible.
HOW OFTEN DOES A TOTAL ECLIPSE HAPPEN?
On average, a total solar eclipse occurs somewhere on Earth every 18 months. The timing for a total eclipse over any specific spot, though, can vary dramatically depending on how the cosmic bodies align. According to Science. com, a ballpark estimate of 400 years is a reasonable average for any given point, but some spots on Earth can take up to 3,600 years between totalities.
WILL I SEE A TOTAL ECLIPSE?
If you live within the path of totality — a relatively narrow strip from Texas to Maine — you will see a total eclipse on April 8. Otherwise, observers in America will see a partial eclipse.
HOW LONG WITH THE ECLIPSE LAST?
At its longest, the April 8 total eclipse will last no more than 4 minutes, 28 seconds, and perhaps considerably shorter depending on the viewing location. The longest eclipses have a duration over 7 minutes.